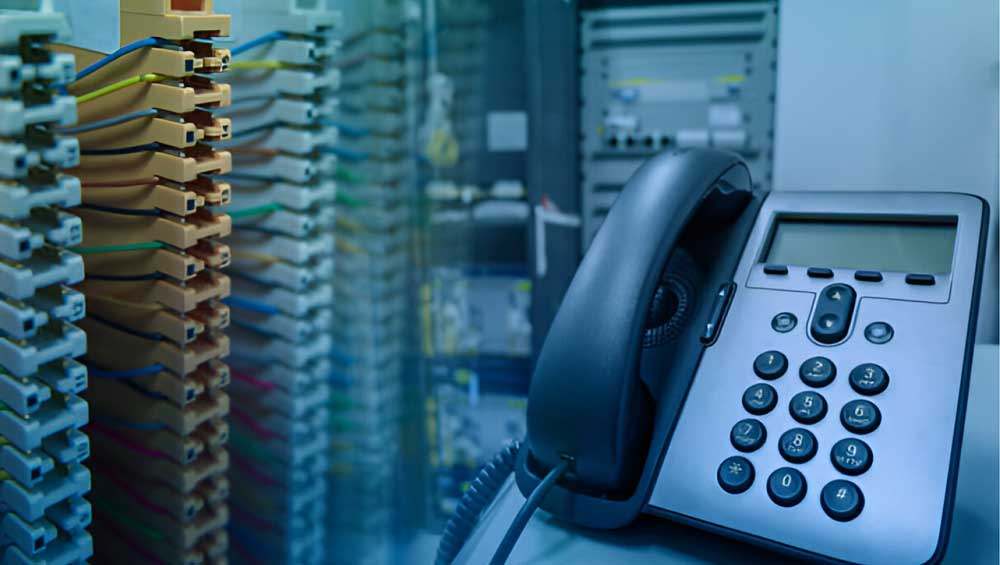
Types of PABX Systems:
Traditional (Analog) PABX:
Description: Uses traditional phone lines (PSTN) to route calls. These systems are hardware-based and require physical phone lines and connections.
Pros: Reliable and can work without an internet connection.
Cons: Higher cost for maintenance and upgrades, limited scalability, and fewer advanced features.
Use Case: Small businesses or older offices that do not require advanced features or VoIP integration.
Digital PABX:
Description: Digital PABX converts analog signals into digital, providing more efficient call handling and advanced features like caller ID, call routing, and conferencing.
Pros: More features and flexibility than analog systems, more efficient call processing.
Cons: Requires specialized hardware and maintenance, although more affordable than traditional systems.
Use Case: Medium to large businesses that want modern features but still rely on traditional telephony.
IP-PBX (Internet Protocol PABX):
Description: Uses VoIP technology to route calls over the internet rather than through traditional phone lines. This type of system integrates with the company’s data network.
Pros: Cost-effective, scalable, can integrate with other digital services (e.g., CRM systems), supports remote work, and offers advanced features like video calling and messaging.
Cons: Requires a stable internet connection, and the initial setup can be complex.
Use Case: Modern businesses, especially those with multiple locations or remote workers.
Hosted/Cloud PABX:
Description: A cloud-based PABX system hosted by a third-party provider. Instead of owning and maintaining the physical PABX hardware, the business accesses the service over the internet.
Pros: Low upfront costs, no maintenance required by the user, easy to scale, supports remote and mobile workforces, and includes all the advanced features of IP-PBX.
Cons: Dependence on internet connectivity and third-party service providers.
Use Case: Startups, small to medium businesses, and organizations that prefer a low-maintenance, scalable, and cost-effective solution.
Benefits of PABX Systems:
Cost Savings: Reduces the need for separate phone lines for each employee by allowing shared access to external phone lines.
Scalability: Easy to add new users and features as the business grows, especially with IP or cloud-based systems.
Improved Communication: Streamlines internal and external communication with features like call routing, voicemail, and conferencing.
Productivity and Efficiency: Employees can easily communicate with each other via internal extensions, while advanced features (e.g., auto-attendant) ensure calls are directed to the right person or department.
Centralized Control: Central management of phone systems for multiple locations or offices, allowing uniform policies and easy oversight.
Key Features of Modern PABX Systems:
- Call Queuing and Call Center Capabilities: Allows businesses to manage high volumes of incoming calls efficiently, with options to prioritize certain calls or route them to the correct agents.
- Mobile Integration: IP-PBX and cloud systems often offer mobile app integration, allowing employees to make and receive calls on their smartphones as if they were at their desk.
- Unified Communications: Integrates voice, video, messaging, and collaboration tools into one platform.
- SIP Trunking: Allows businesses to connect their PABX system to VoIP services for lower-cost international or long-distance calls.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud-based PABX systems can offer automatic failover solutions, ensuring that calls are redirected in the event of a network outage.